 What is 3D Printing?
What is 3D Printing?
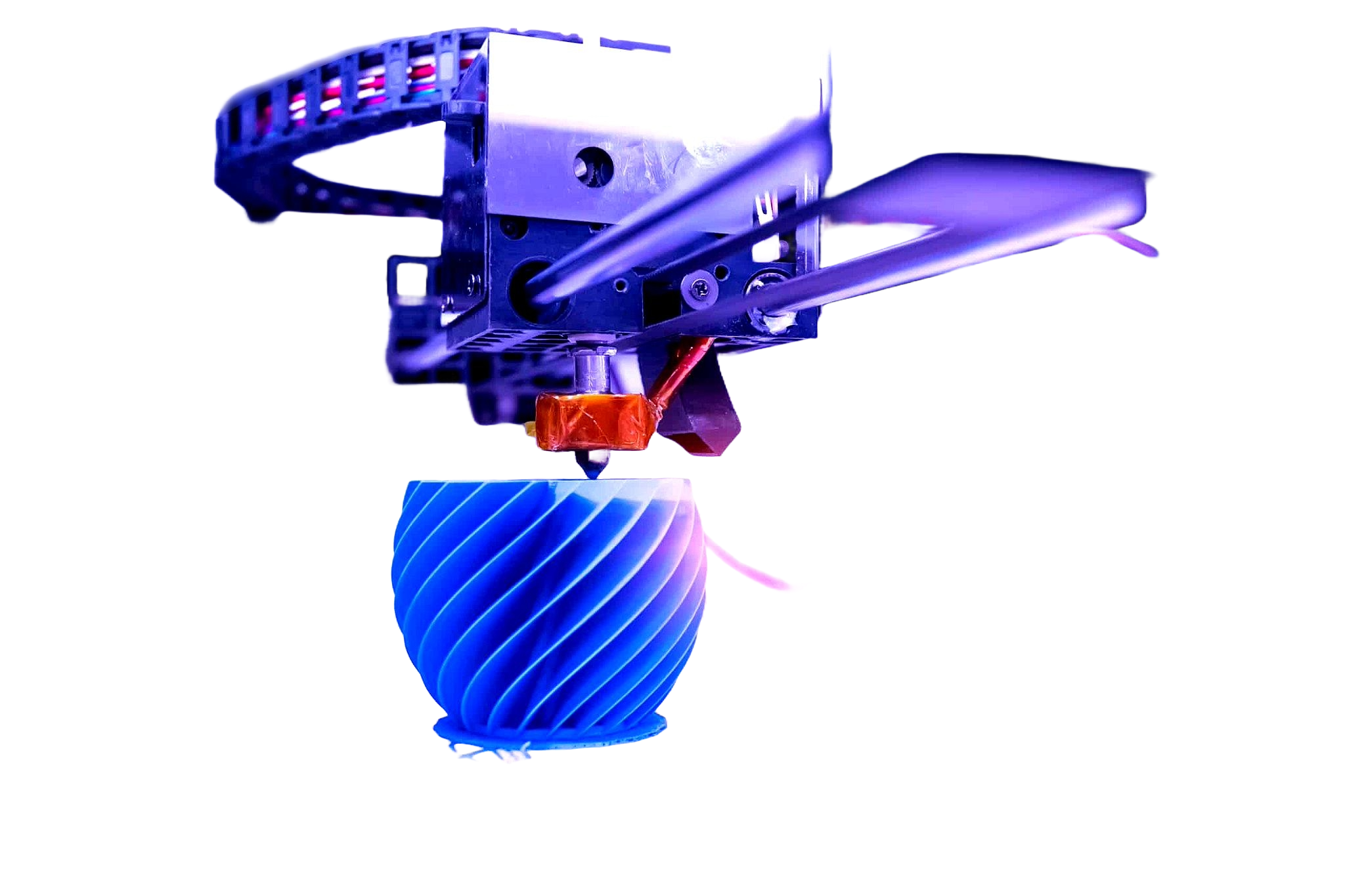
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a revolutionary technology that allows objects to be created layer by layer from digital designs. Unlike traditional manufacturing, which often involves cutting, molding, or assembling materials, 3D printing builds objects from the ground up using materials such as plastic, resin, metal, or even biodegradable compounds.
How Does 3D Printing Work?
The process starts with a digital 3D model, typically created using computer-aided design (CAD) software. This model is then sliced into thin layers, which the 3D printer reads and prints one by one. The printer deposits material in precise locations, gradually forming the final object.
Applications of 3D Printing
3D printing is used in various industries, including:
- Prototyping & Manufacturing – Companies use it to develop prototypes quickly and reduce production costs.
- Medicine & Healthcare – Custom prosthetics, dental implants, and even bioprinting of tissues are becoming more common.
- Architecture & Construction – 3D-printed models help architects visualize projects, and even full-scale buildings are being printed.
- Education & Hobbyists – Schools and makers use 3D printing for learning and personal projects.
The Future of 3D Printing
As technology advances, 3D printing is becoming more accessible and affordable. From personalized products to sustainable solutions, the possibilities are endless. Whether you're a business or an individual, 3D printing opens up exciting new ways to create, innovate, and bring ideas to life.









